Websites should feel as quick and seamless as mobile apps, according to modern consumers.
Single Page Applications (SPAs) do just that. SPAs refresh content instantaneously within a single browser window, in contrast to traditional websites that reload the entire page whenever something changes.
They are now a common choice for many cutting-edge online platforms, like food delivery applications and streaming services, thanks to this flawless experience.
This article, “A Beginner’s Guide to Creating Single Page Applications (SPAs) – Step-by-Step Tutorial,” is written especially for novices who are interested in learning how these incredibly quick web applications function.
This Single Page Application tutorial for beginners will lead you through the fundamentals in a useful and approachable manner, regardless of whether you are a student investigating frontend development for the first time or a career switcher hoping to create actual, contemporary online applications.
Along with learning the fundamental ideas underpinning SPAs, you will also discover the precise tools and techniques used by developers today, such as routing, reusable components, JavaScript principles, API communication, and browser-based performance advancements.
We will create a basic project using well-known starting frameworks like React, providing you with a step-by-step SPA instruction for students who prefer practical learning over theory.
By the end of this tutorial, you will know how SPAs work behind the scenes and be able to construct, launch, and demonstrate your own modern web application, which is an important milestone for anyone starting out in frontend development today.
What is a Single Page Application (SPA)?
Instead of requesting and reloading entirely new pages from the server, a Single Page Application (SPA) is a web application that loads a single HTML page once and then dynamically updates the content using JavaScript. Because of this, the user experience is quick, seamless, and app-like.
Every time a user clicks a link on a standard website, also known as a Multi-Page Application (MPA), the browser submits a new request to the server, downloads a new HTML page, and replaces the entire content on the screen.
It can feel slow to constantly reload the entire page, especially on devices or networks that are not as strong.
A single-page application, on the other hand, functions differently. The browser downloads the essential HTML, CSS, and JavaScript only once when the user initially launches the SPA.
After that, the following happens –
- Within the browser, users can navigate between “pages” (such as Home, About, and Dashboard).
- Routing is handled by JavaScript, which determines which view or component should be displayed.
- APIs (typically JSON) are used to get only the necessary data from the server.
- The DOM (Document Object Model) is dynamically updated, so only a portion of the screen changes rather than the complete site.
Because the browser isn’t continually discarding and reconstructing entire pages, SPAs feel incredibly quick and responsive. It is upgrading only what is necessary while reusing the same shell.
It is helpful to consider an SPA as a single container page that behaves like numerous pages by displaying and hiding various components in response to user interaction and URL changes, as seen from the viewpoint of a beginner following this Single Page Application tutorial.
Read Also: Common Web Development Mistakes Developers Make And How To Avoid Them
How an SPA Loads Content Dynamically
An SPA functions in the concept of client-side rendering. Here is how it works.
The server sends a simple HTML file that includes links to JavaScript and CSS.
The JavaScript framework (such as React, Vue, or Angular) runs in the browser, creates the UI with components, and responds to user activities (clicks, form submissions, navigation).
When new data is required (for example, a list of products or user information), the SPA queries a REST API or GraphQL API, receives a JSON answer, and updates only the relevant sections of the page.
Instead of seeing a blank white flash or a complete browser reload, the user experiences seamless, quick transitions. This dynamic technique is precisely what you will use later in this detailed SPA guide.
SPA vs Traditional Websites (MPAs)
The distinction between an SPA and an MPA is not solely about speed; it is also about where the work takes place.
In a conventional MPA, the server is in charge of generating the entire HTML for every page, managing the majority of page transitions, and consistently delivering the entire document to the browser.
The majority of the page rendering in a single-page application is handled by the browser and JavaScript, which also fetches only the necessary data rather than a complete new page and changes views as the user navigates.
For novices, this means that rather than creating numerous distinct HTML pages, SPAs need you to spend more time implementing frontend JavaScript functionality (components, state, routing, and API calls).
For straightforward, content-rich, SEO-focused websites like blogs or news portals, MPAs may be a preferable option.
SPAs excel in social networks, SaaS tools, interactive dashboards, and contemporary web apps where users spend a lot of time on the site interacting with the interface.
Visualizing SPA Architecture (Diagram Explanation)
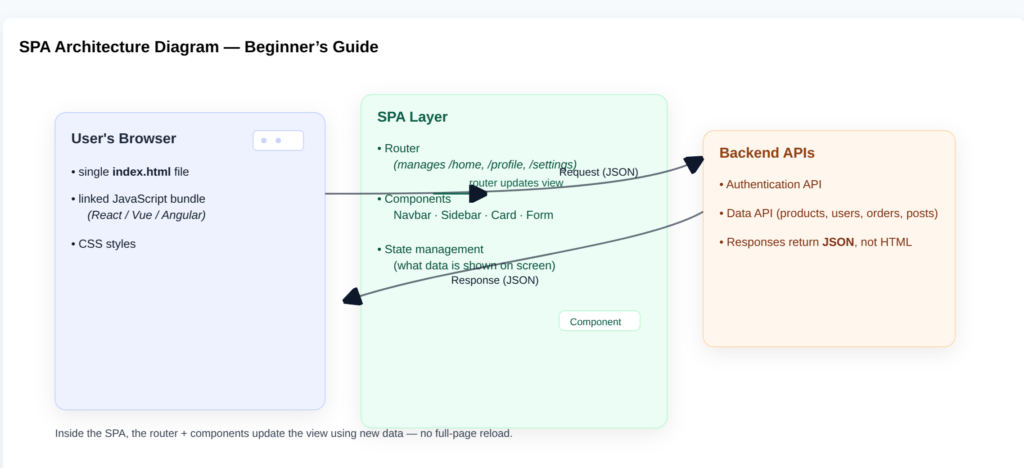
Read Also: Best JavaScript Courses on Coursera
How Do SPAs Work Behind the Scenes?
Understanding the inner workings of Single Page Applications (SPAs) is crucial to comprehending why they feel quick and contemporary.
SPAs transfer the majority of the user interface (UI) work to the browser through a process known as client-side rendering, rather than relying on the server to construct and send new pages.
That transformation is described in detail in this section of our Single Page Application tutorial for beginners.
Client-Side Rendering: The Engine of SPAs
Every time a user clicks on a link on a traditional website, the server creates an entire page and transmits it to them. Here’s how SPAs turn this model on its head.
A single HTML file, a JavaScript bundle with application functionality, and CSS styles for layout and design are downloaded by the browser during the initial visit.
After that, the browser is responsible for managing UI changes, presenting various pages, and updating data without requiring page loads.
As a result, the application remains in memory, enabling quick screen changes that mimic those of a native mobile application. It is one of the main reasons SPAs are so well-liked by both novice and seasoned developers.
JavaScript Frameworks That Make SPAs Possible
SPAs rely on powerful frameworks like:
- React (most popular and beginner-friendly)
- Vue.js (simple learning curve)
- Angular (enterprise features built-in)
- Svelte (compiler-based efficiency)
These frameworks manage routing, enabling URLs like /home or /about without requiring a page reload, track state (what data should be displayed on the screen), and divide the interface into reusable components.
You will construct your user interface (UI) by assembling these elements like Lego bricks as you follow this detailed SPA guide.
Fetching Data Dynamically Using APIs
SPAs retrieve data only from the server rather than entire pages. Only the necessary portion of the screen is updated by SPAs when they make background calls known as AJAX queries. Servers reply using JSON.
As an illustration, a dashboard may retrieve the most recent user notifications without interfering with the user’s present task.
This makes it possible to use less bandwidth, navigate quickly and smoothly, and have better experiences on mobile and low-speed connections.
DOM Updates and Performance Optimization
JavaScript effectively modifies the DOM, and only the affected UI elements update when the SPA receives new data.
React and other frameworks use a virtual document object model (DOM), which allows them to update only the specific areas of the actual page that have changed after tracking changes in memory.
Consistent 60 FPS interactions, fewer layout reflows, and a solid and interactive user interface are the outcomes of this.
Additionally, code splitting (smaller scripts for faster load), lazy loading (load features only when needed), and smart caching (reuse fetched data) are ways that modern SPAs increase performance.
Read Also: Practical Web Development Projects For Beginners – Start Building Today
SPA vs MPA — Which One Should You Build?
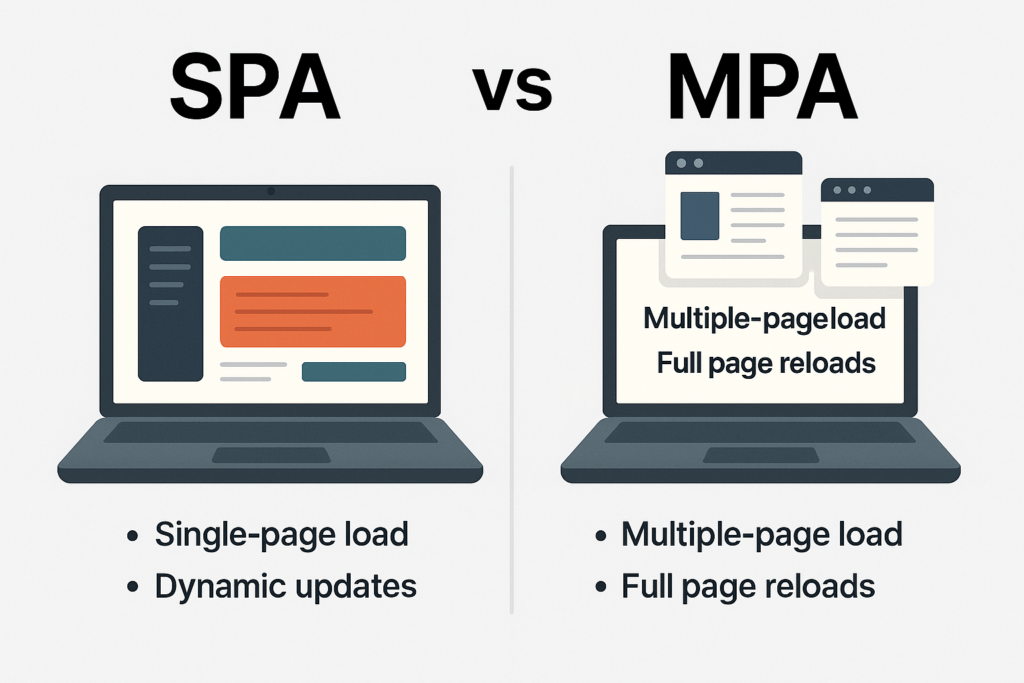
It’s important to comprehend the differences between Single Page Applications (SPAs) and Multi-Page Applications (MPAs) before delving further into the development process.
MPAs use the conventional approach, loading a new HTML page straight from the server with each navigation, but SPAs use client-side rendering and refresh content dynamically inside the browser.
Every user activity that modifies the view causes a full-page load from the server in an MPA website structure.
Consider e-commerce sites, blogs, or banking websites that have a lot of distinct pages.
Large websites with several structured page kinds and content that is SEO-focused are excellent candidates for this paradigm.
However, because the browser must discard and refresh information on each navigation, MPAs may appear slower compared to well-optimized SPAs.
SEO, Speed, and Maintenance: What Really Matters
Because just the essential UI modifications take place, SPAs are excellent at speed and interactivity. They provide app-like experiences and nearly instantaneous changes.
However, as search engines favor server-rendered HTML, this method places more processing on the browser, which may result in a slightly slower initial load and SEO issues.
MPAs are naturally SEO-friendly, easier to maintain for content-heavy organizations, and by default, they have less exposure to client-side scripts than SPAs.
However, when creating highly dynamic chat interfaces, dashboards, or apps that need real-time updates, MPAs can get complicated.
In summary, MPAs offer better ranking, particularly for informational websites, whereas SPAs offer better user experience for web apps.
SPA vs MPA: Quick Comparison Table
| Feature | SPA (Single Page Application) | MPA (Multi-Page Application) |
|---|---|---|
| Page Loads | Single load, dynamic content updates | Full page reload on each navigation |
| Speed & UX | Very fast once loaded | Slower transitions |
| Rendering | Client-side rendering | Server-side rendering |
| SEO | Requires extra work (SSR, prerendering) | Naturally SEO-friendly |
| Development | More JavaScript complexity | Traditional page-by-page structure |
| Best For | Dashboards, SaaS apps, feeds, social apps | Blogs, portfolios, e-commerce catalogs |
This comparison makes one thing clear: the right choice depends on your goals.
Read Also: Best NodeJS Courses and Certifications for Developers
Benefits of Building Single Page Applications
You’ll see why SPAs have become the foundation of contemporary web development as you work through this Single Page Application tutorial for beginners.
They enable developers to create web experiences that are quick, easy to use, and scalable—qualities that consumers now demand.
The main benefits that make SPAs a popular option for professionals and students pursuing frontend development are listed below.
Fast Navigation and Improved User Experience
Speed is the primary benefit of SPAs. Unlike MPAs, which require several full-page reloads, navigating occurs quickly as the browser loads the first page.
Only what is required is dynamically updated by the program, resulting in responsive, fluid, and seamless transitions.
In settings where users remain engaged, such as social networks, dashboards, online tools, and messaging platforms, this improved user experience (UX) is particularly crucial.
Fast-spinning material improves user pleasure, conversion, and retention while keeping users interested for longer.
Reusable Components That Save Time and Effort
Using frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular, SPAs are constructed with reusable, modular components.
Every component of the user interface (UI), including buttons, product cards, forms, and navigation bars, can be made once and utilized again throughout the program.
This method speeds up the development of repetitive code, guarantees a uniform user interface across all views, and facilitates project scaling and editing.
High Demand in Modern Development and Job Markets
SPA frameworks are being rapidly adopted by businesses in India and throughout the world to increase productivity and scalability.
Job positions, including Frontend Developer, React Developer, UI Engineer, and Full Stack Developer, are accessible to those with React, Vue, or Angular skills.
Many contemporary user-facing systems, including Indian firms like Paytm, Zomato, and Swiggy adopt SPA-style design to maintain quick user interfaces.
Compared to antiquated methods, learning SPAs gives new hires improved career momentum and helps them fit with contemporary hiring demands.
Better Caching and Offline Capabilities (PWA Advantage)
Using caching techniques like Local Storage, IndexedDB, and Service Workers (Progressive Web Apps), SPAs can store crucial data directly in the browser.
Pages load nearly instantly after they are cached, even when network access is poor. PWA improvements allow SPAs to function offline, send alerts, and be installed similarly to mobile apps.
Web reach and app performance are combined to create the best of both worlds.
Limitations of SPAs (and How to Overcome Them)
Although Single Page Applications (SPAs) enable developers to create quick and captivating user experiences, novices should be aware of the architectural difficulties associated with this method.
Understanding these constraints enables you to create more intelligent, scalable applications.
The main disadvantages of SPAs are listed below, along with workable methods that are employed in contemporary development to overcome them.
SEO Challenges and Server-Side Rendering (SSR) Solutions
Because SPAs rely on client-side rendering, JavaScript is used in the browser to create the majority of the content.
Crawlers for search engines like HTML material that is sent straight from the server. Thus, it may be difficult for unconventional SPAs to rank for competitive search phrases.
But frameworks now come with built-in fixes, which are as follows.
- Search engines are guaranteed to receive completely rendered HTML thanks to Server-Side Rendering (SSR) with Next.js (React) or Nuxt (Vue).
- For important pages, prerendering techniques produce static HTML snapshots.
- SEO-critical pages can be server-rendered using hybrid rendering techniques, with the remaining sites operating as conventional SPAs.
Nowadays, the majority of SPA teams use SSR or SSG in a professional setting to preserve SEO performance without compromising seamless UX.
Initial Load Time Concerns
Compared to classic MPAs, SPAs send more JavaScript up front. Particularly on low-end devices or slow networks, this first download may cause the first page to load more slowly.
Developers use code splitting (load only what is needed for each route), lazy loading (fetch components and data when needed), asset compression (using Brotli/GZIP), and caching (using service workers and the browser’s storage capabilities) to handle this.
Navigation becomes much faster than MPAs after the SPA is bootstrapped, making the initial wait worthwhile.
Security Considerations
Compared to server-rendered webpages, SPAs expose more JavaScript because logic and routing are handled in the browser.
As a result, they are susceptible to frequent client-side attacks such as token theft, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), and API misuse.
Development teams rely on proper input sanitization to reduce these hazards, rate-limiting and authenticity checks on backend APIs, HTTPS enforcement, and secure authentication workflows (OAuth, JWT with brief lives).
As long as frontend and backend security measures are strictly maintained, security is still controllable.
Routing Complexities
Because SPA routing is entirely virtual, the server is unaware of the route that the user is attempting to visit.
If the server is not set up to consistently return the SPA’s base index.html, directly navigating to a deeper path like /profile may result in a 404.
Enabling history API fallback in deployment platforms like Netlify or Vercel, utilizing routers like React Router or Vue Router that appropriately handle URLs, and carefully mapping protected routes with authentication guards are the solutions to this problem.
Routing becomes secure and predictable with the correct tools, all without sacrificing the advantages of fast navigation.
Step-by-Step Tutorial: Build Your First SPA
It’s time to put theory into action now. You will actually construct a simple React-based SPA from scratch in this portion of A Beginner’s Guide to Creating Single Page Applications (SPAs) – Step-by-Step Tutorial.
Use this as a step-by-step SPA guide for students and novices. If you follow each step in the correct order, you will have a functional project that you can share.
Step 1: Set Up Your Development Environment
To build a modern Single Page Application, you need three essentials: Node.js, npm, and a code editor.
Node.js is a runtime JavaScript environment that executes code outside the browser. You need to install the latest version of this tool from the official website.
npm (Node Package Manager) comes with Node.js, which allows you to install essential libraries and tools that you may need while building this project.
Next comes a code editor. You can download and install the Visual Code Editor or any good code editor, as per your choice.
After that, open your terminal and confirm that these tools are installed and running.
Step 2: Create Components and UI Layout
Components are tiny, reusable UI elements that build SPAs. React’s components are often straightforward functions that return JSX, which is JavaScript’s HTML-like syntax.
First, create a file named Home.jsx inside src/.
function Home() {
return (
<section>
<h1>Welcome to My First SPA</h1>
<p>This is a simple Single Page Application built with React.</p>
</section>
);
}
export default Home;
Then create another component named About.jsx.
function About() {
return (
<section>
<h1>About This App</h1>
<p>This SPA shows how to use components, routing, and APIs.</p>
</section>
);
}
export default About;
Use these two components in App.jsx.
import Home from "./Home";
import About from "./About";
function App() {
return (
<div>
<header>
<h2>My First React SPA</h2>
</header>
<main>
<Home />
<About />
</main>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Once you do this, you will have reusable components that form the basic layout of your SPA.
Because JSX allows you to create HTML-like code directly in JavaScript, it’s a very user-friendly method of structuring a single-page application.
Step 3: Add Routing to Your SPA
All content is currently shown simultaneously. A genuine SPA displays various “pages” according to the URL without requiring a reload. React Router is useful in this situation.
Now, install the React Router.
Then, update main.jsx to wrap your app in a router.
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom/client";
import { BrowserRouter } from "react-router-dom";
import App from "./App.jsx";
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root")).render(
<BrowserRouter>
<App />
</BrowserRouter>
);
Now, define routes in App.jsx.
import { Routes, Route, Link } from "react-router-dom";
import Home from "./Home";
import About from "./About";
function App() {
return (
<div>
<header>
<h2>My First React SPA</h2>
<nav>
<Link to="/">Home</Link> | <Link to="/about">About</Link>
</nav>
</header>
<main>
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<Home />} />
<Route path="/about" element={<About />} />
</Routes>
</main>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Once you’ve completed this, select “Home” or “About.” You’ll notice that the page never fully reloads, even though the URL changes.
Multi-section navigation that doesn’t require page reloads and is fully client-side powered is typical SPA behavior.
Step 4: Connect to an API
An effective SPA needs to communicate with the external world. You will retrieve user data from a public API and dynamically render it in this section of the Single Page Application tutorial for beginners.
Now, create Users.jsx.
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
function Users() {
const [users, setUsers] = useState([]);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true);
const [error, setError] = useState("");
useEffect(() => {
fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users")
.then((res) => {
if (!res.ok) {
throw new Error("Network response was not ok");
}
return res.json();
})
.then((data) => {
setUsers(data);
setLoading(false);
})
.catch((err) => {
setError("Failed to load users");
setLoading(false);
});
}, []);
if (loading) return <p>Loading users...</p>;
if (error) return <p>{error}</p>;
return (
<section>
<h1>User List</h1>
<ul>
{users.map((user) => (
<li key={user.id}>
<strong>{user.name}</strong> – {user.email}
</li>
))}
</ul>
</section>
);
}
export default Users;
Then, register the route in App.jsx.
import Users from "./Users";
// inside <nav>:
<nav>
<Link to="/">Home</Link> | <Link to="/about">About</Link> |{" "}
<Link to="/users">Users</Link>
</nav>
// inside <Routes>:
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<Home />} />
<Route path="/about" element={<About />} />
<Route path="/users" element={<Users />} />
</Routes>
Now your SPA:
- Fetches user data from an external API
- Handles loading state
- Displays a friendly error message if something fails
- Updates only the relevant part of the page—no reload, no interruption
This is the core pattern behind most real-world SPAs: fetch → render → update.
Step 5: Deploy Your SPA
Deployment is the last stage in this comprehensive SPA guide for students. Your Single Page Application should have a shared URL and be open to the world.
Option 1: Deploy with Netlify
First, create a production build.
You may either connect your Git repository and allow Netlify auto-build, or you can drag the created dist/ (Vite) or build/ (CRA) folder onto Netlify’s dashboard.
Turn on “Single Page Application” functionality by rerouting all routes to index.html. Usually, Netlify provides this through a UI option or a _redirects file.
A live URL similar to https://my-first-spa.netlify.app will be sent to you.
Option 2: Deploy with Vercel
Install and connect your GitHub repository to Vercel CLI.
Upload the code to GitHub.
In Vercel, import the project and choose the appropriate framework (Vite or React).
Vercel builds and launches on its own.
A URL similar to https://my-first-spa.vercel.app will be sent to you.
Once your single page application is deployed, you can share the link with your friends, educators, and recruiters.
Also, you can add it to your portfolio to showcase that you understand what SPAs are and have built real applications from scratch.
Popular SPA Frameworks for Beginners
Modern Single Page Applications (SPAs) are created by developers using powerful JavaScript frameworks that make state management, routing, and UI rendering easier.
Selecting the appropriate framework can influence both your educational path and future employment prospects, according to this Single Page Application tutorial for beginners.
To assist you in making an informed decision, the four most widely used SPA technologies are briefly described below, together with their obvious benefits and drawbacks.
React — The Best Starting Point for Beginners
The industry leader and top pick for aspiring front-end engineers is React (by Meta). It ensures quick dynamic UI updates by utilizing components, hooks, and a virtual DOM.
Why beginners love it
- Strong community and ecosystem support
- Most job vacancies in India and throughout the world
- Adaptable design using countless libraries (such as React Router for navigation)
Consideration
- It may seem disorganized; novices must select tools for deployment, routing, and state.
Read Also: Best React Courses On Coursera
Vue.js — Simplest Learning Curve
If you are familiar with HTML and JavaScript, Vue.js offers an easy-to-use syntax that is suitable for beginners. It minimizes boilerplate code while preserving a component-driven architecture.
Pros
- Easiest framework for learning component rendering
- Lightweight with excellent documentation
- Great for small to medium projects
Cons
- Slightly smaller job market compared to React
- Large-scale architecture requires additional tools
Angular — Enterprise-Level Power
Angular, which was developed and supported by Google, offers a full solution right out of the box, including a powerful CLI, routing, HTTP connectivity, form handling, and TypeScript support by default.
Pros
- Highly structured architecture for large applications
- Ideal for enterprise environments and long-term maintenance
- Great integration with TypeScript improves reliability
Cons
- Steeper learning curve due to advanced concepts
- More opinionated and heavier compared to React or Vue
Read Also: Best Angular Courses on Coursera
Svelte — Modern Simplicity
Svelte takes a different approach by compiling your components into highly optimized vanilla JavaScript during the construction phase rather than using client-side heavy rendering.
Pros
- Minimal code with fast performance
- Small bundle sizes and quicker initial load
- Very beginner-friendly syntax
Cons
- Smaller job ecosystem
- Fewer enterprise-grade tools and libraries
Real-World Examples of SPAs
Some of the most popular platforms in the world are powered by single-page applications, making them more than just a learning exercise.
SPAs are frequently the primary architectural option when customers expect quick response, seamless navigation, and an app-like experience on the web.
Here are actual examples from IT giants from India and around the world to help make this Single Page Application tutorial more applicable.
Popular SPA Examples in India
SPAs have been adopted by India’s rapidly evolving digital ecosystem to provide speed under inconsistent network conditions. Listed below are a few noteworthy examples.
- Zomato (Web App)
The SPA-style web interface of the restaurant discovery and meal delivery platform allows users to explore menus, track orders, and switch views instantly—perfect for real-time updates.
- Swiggy (Web App)
Swiggy’s browser-based ordering system depends on updates that are driven by dynamic APIs. Only the necessary content reloads when users search dishes or apply filters, ensuring seamless navigation even on mobile data.
Since millions of people use these apps every day, interactivity and performance are crucial. They can efficiently manage frequent user interactions without annoying delays thanks to SPA-like patterns.
Global SPA Success Stories
Because they require scalability and reactivity, international tech businesses have been early users of SPA technology.
- Gmail
Email interactions, including opening messages, searching, and changing inbox tabs, happen quickly without requiring page refreshes. Even in the browser, it has the sense of a desktop application.
- Netflix Web Interface
The interface uses client-side rendering and intelligent caching to dynamically load posters, movies, and suggestions based on user actions and preferences.
- Trello
A project-board application that uses a component-based user interface to rapidly update each drag-and-drop action. It wouldn’t work as a conventional page-reloading interface.
These are only a few examples: many websites use SPA-style web interfaces for high engagement and real-time interactions.
Why Businesses Choose SPA Architecture
Companies choose Single Page Applications because they directly support business goals.
- Higher user engagement
Smooth browsing increases session duration and reduces bounce rates.
- Better conversion rates
Instant UI responses prevent drop-offs during key actions (checkout, login).
- Scalability and reusability
Component-based development speeds up product iterations.
- Cross-platform capabilities
A single SPA codebase can evolve into a Progressive Web App (PWA), making it installable like a mobile app.
- Real-time experiences
SPAs are ideal for chats, dashboards, content streams, and collaborative tools.
Career Opportunities in SPA Development
Learning to code is only one aspect of building SPAs; it also opens up a number of professional responsibilities and career paths, especially in the Indian tech sector.
Here are some examples of how being proficient in SPAs might impact your career, typical pay, and what other abilities will help you stand out.
Common Job Roles in India
People who master SPA skills can apply for job roles like Front-end developer and React Developer.
With time, they will get experience in the field and get promoted to job roles like UI Engineer and Full-stack Developer.
Salary & Market Demand (India Context)
Entry-level developers who work in the SPA domain get around ₹3-6 LPA.
Mid-level developers, when they gain some experience in the field, can expect ₹8-15 LPA. However, this depends on skills, project complexity, and location.
More experienced developers who work in senior positions can expect ₹12-25 LPA or more.
These salary ranges are approximate and can vary depending on the company, city, tech-stack, nature of the project, and your skills.
Conclusion
Single Page Applications (SPAs) provide the speed, seamless transitions, and quick responses that modern users demand from websites.
You learned what SPAs are, how they operate in the background, and why companies depend on them to produce captivating digital products throughout this comprehensive SPA guide for students and novices.
Faster navigation, reusable components, offline functionality, and a direct link to in-demand positions like Frontend Developer and React Developer in India and throughout the world are just a few of the practical advantages you witnessed.
More significantly, you now possess the fundamental knowledge and abilities needed to construct your first SPA, including configuring a contemporary development environment, building components, implementing routing, retrieving data from APIs, and deploying to the web.
These are the precise skills that employers seek out in fresh frontend talent.
What do you do next? By delving further into framework features, performance optimization, and practical tools like Next.js, server-side rendering, authentication, and DevOps workflows, you may further hone your skills.
You are getting closer to being a self-assured, marketable web developer with each advancement you make.
Which SPAs are you using in your daily life? Name them in the comment section.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Single Page Application?
A Single Page Application (SPA) is a type of web application that loads a single HTML page once and uses JavaScript to dynamically update content without requiring a page refresh. SPAs are perfect for contemporary, highly interactive web platforms because they produce quicker navigation, more fluid interactions, and an app-like experience right in the browser.
Is SPA development suitable for beginners?
Yes. Important frontend skills like components, routing, state management, and API integration are taught through SPA development. Beginners get hands-on experience with real-world web architecture, which facilitates their transfer into professional positions like front-end or React developers. A solid foundation for web development job advancement is provided by learning SPAs early on.
Best framework for building SPAs as a beginner?
React’s extensive ecosystem, community support, and high demand for jobs in India and throughout the world make it the ideal place to start. Angular works well in corporate settings, but Vue’s straightforward syntax makes it suitable for beginners. Beginners can create useful SPA projects that are in line with current recruiting trends and industry needs by starting with React.
Are SPAs good for SEO?
Because content is rendered client-side, SPAs are not naturally SEO-friendly. However, SPAs can become fully crawlable and SEO-ready by utilizing server-side rendering (SSR), static site generation (SSG), or prerendering with frameworks like Next.js. SPAs may retain quick user experiences while achieving high rankings with the proper configuration.
Are SPAs used in India for tech jobs?
Definitely, major websites like Zomato, Swiggy, Flipkart, and Paytm use SPA-style frontends, which enable them to provide rapid, engaging online experiences. React, Angular, and Vue developers are highly sought after by businesses in India. The majority of contemporary frontend positions in the Indian tech sector involve SPA development.
Share Now
More Articles
Best NextJS Courses and Certifications for Developers
Best Website Builders for Beginners
Discover more from technicalstudies
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.